Search in dictionary
Foot lesser yáng (shào yáng) gallbladder channel
足少阳胆经 〔足少陽膽經〕 zú shào yáng dǎn jīng
Abbreviation: GB. One of the twelve channels.
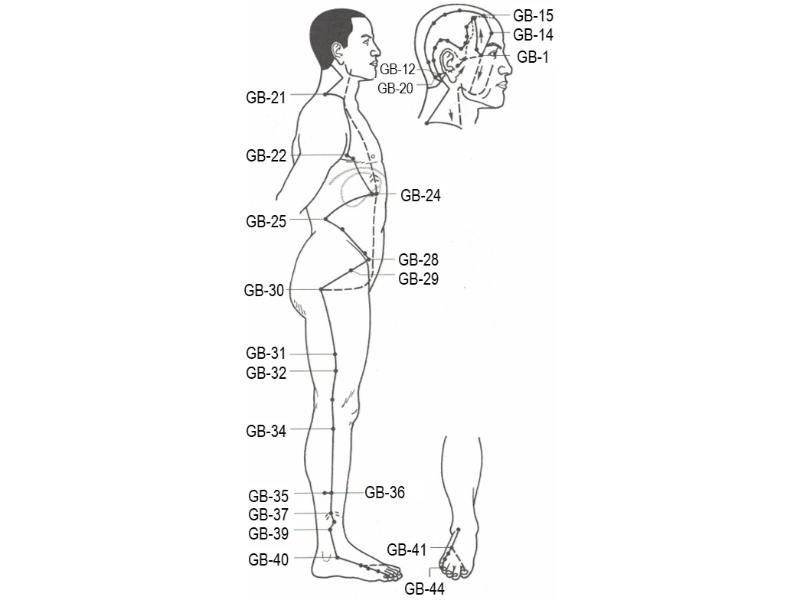 |
| Foot lesser yáng (shào yáng) gallbladder channel |
|---|
Connections
TB → GB → LR; homes to the gallbladder; nets the liver.
Gallbladder Channel Pathway
Overview
Outer canthus → corner of forehead → mastoid process → above eyebrow → below occipital bone → GV-14 → supraclavicular fossa. - Branch (1): Behind the ear → ear → in front of ear → outer canthus.
- Secondary branch (2): Outer canthus → lower jaw → below the eye socket → corner of jaw → behind supraclavicular fossa (rejoining the main channel pathway).
- Main pathway:
Supraclavicular fossa → side of chest → hip joint → side of leg → lateral malleolus → dorsum of foot → lateral tip of fourth toe. - Branch (3): Dorsum of foot → lateral tip of great toe → LR.
Description
The foot lesser yáng (shào yáng) gallbladder channel starts from the outer canthus (GB-1, tóng zǐ liáo, Pupil Bone-Hole), rises to the corner of the forehead (GB-4, hàn yàn, Forehead Fullness), turns back to the mastoid process of the occipital bone behind the ear (GB-12, wán gǔ, Completion Bone), turns forward again over the head and forehead to a point above the eyebrow (GB-14, yáng bái, Yáng White), turns back again over the head to GB-20 (fēng chí, Wind Pool) just below the occipital bone, descends to GV-14 (dà zhuī, Great Hammer). It then descends the lateral face of the neck, crosses the hand lesser yáng (shào yáng) triple burner channel, turns backward across the triple burner channel again, before finally running forward into the supraclavicular fossa.
A branch (1) separates from the main channel behind the ear. It enters the ear, remerges in front to it, and runs to behind the outer canthus.
A secondary branch (2) that separates at the outer canthus descends to the lateral aspect of the lower jaw (ST-5, dà yíng, Great Reception), meeting with the branch line of the hand lesser yáng (shào yáng) that passes over the face. It ascends to below the eye socket and runs downward over the corner of the mandible and the neck to rejoin the main GB channel pathway behind the supraclavicular fossa. From here, it enters the trunk, passes through the diaphragm, nets the liver, and homes to the gallbladder, passes along the inside of the rib-side, surfaces at the qì street (气街 qì jiē, i.e., the area of the pulsating vessel in the groin), skirts around the pubic hair region, before moving laterally into the lateral hollow of the buttock at the hip joint (GB-30, huán tiào, Jumping Round).
From the supraclavicular fossa, the main pathway descends to the armpit, down the side of the chest, over the floating ribs to GB-24 (日月 rì yuè, Sun and Moon). It descends laterally to GB-25 (京门 jīng mén, Capital Gate) in the flank region, then medially to GB-28 (wéi dào, Linking Path), and then laterally again to the hip joint (GB-30 huán tiào, Jumping Round) to meet the branch line and on down to (2). It then descends the lateral aspect of the thigh and knee, down the lower leg in front to the fibula to the end of the fibula, to emerge in front of the lateral malleolus. It passes over the dorsum of the foot, to the lateral tip of the fourth toe (GB-41, zú lín qì, Foot Overlooking Tears).
A branch (3) separates on the dorsum of the foot (GB-41, zú lín qì, Foot Overlooking Tears), proceeding forward to the lateral tip of the big toe and then turning back under the nail to spread over the tuft of hair behind the nail of the big toe, where it meets the foot reverting yīn (jué yīn) liver channel at LR-1 (大敦 dà dūn, Large Pile).
Gallbladder Channel Acupoints
Indications of GB Acupoints
The 44 points on the foot lesser yáng (shào yáng) gallbladder channel treat diseases of the head, ears, eyes, throat, spirit-mind, externally contracted febrile disease, and other conditions in areas traversed by the channel.
- Head, ears, eyes, throat: Headache, dizzy vision, pain in the outer canthus, nasal congestion, bitter taste in the mouth.
- Malarial disease.
- External pathway: Pain and swelling in the supraclavicular fossa; swollen armpits; pain along the lateral aspect of the rib-side, hip, thigh, knee, or lower legs; wilting or impediment of the lower limbs (including sciatica in biomedicine).
Major GB Acupoints
GB-20 (风池 fēng chí, Wind Pool): Located on the posterior aspect of the neck, below the occipital bone, in the large depression between the trapezius and the sternocleidomastoid muscles.
- Indications: Headache; dizzy vision; painful red swollen eyes; deep-source nasal congestion; sniveling and nosebleed; tinnitus; painful stiffness of the neck and nape; common cold; epilepsy; wind stroke; goiter; febrile disease; malarial disease; goiter.
- Stimulus: Needling: 0.5–1. 0 cùn perpendicular insertion. Moxa: 3–7 cones; pole 5–20 min.
- Categories: Intersection point (jiāo huì xué) of the gallbladder channel and yáng linking (yáng wéi) and yáng springing (yáng qiāo) vessels.
GB-34 (阳陵泉 yáng líng quán, Yáng Mound Spring): Located on the lateral aspect of the lower leg, in the depression immediately anterior and inferior to the head of the fibula.
- Indications: Rib-side pain; bitter taste in the mouth; retching and vomiting; wilting-impediment (wěi bì) of the lower limbs; leg qì (beriberi); jaundice; child fright wind.
- Stimulus: Needling: 0.8–1.2 cùn perpendicular insertion. Moxa: 5–7 cones; pole 20–30 min.
- Categories: Uniting (hé) (earth) point; meeting point (huì xué) of the sinews; one of Mǎ Dān-Yáng’s twelve heavenly star points.
| Indications for GB Points |
|---|
|
GB-39 (悬钟 xuán zhōng, Suspended Bell): Located on the lateral aspect of the lower leg, 3 cùn superior to the tip of the lateral malleolus, immediately posterior to the lateral crest of the fibula in the narrow space between the bone and the peroneus brevis tendon.
- Indications: Stiff nape; distension and pain in the chest and rib-side; wilting-impediment (wěi bì) of the lower limbs; painful swollen throat; leg qì (beriberi): hemorrhoids.
- Stimulus: Needling: 0.4–0.5 cùn perpendicular insertion. Moxa: 3–5 cones; pole 5–20 min.
- Categories: Meeting point (huì xué) of the marrow.
GB-41 (足临泣 zú lín qì, Foot Overlooking Tears): Located on the dorsal aspect of the foot, between the fourth and fifth metatarsal bones, on the lateral (proximal) side of the extensor digitorum longus tendon that attaches to the little toe.
- Indications: Painful red swollen eyes; rib-side pain; menstrual irregularities; enuresis; mammary welling-abscess (rǔ yōng); scrofula; painful swelling of the dorsum of the foot; malarial disease.
- Stimulus: Needling: 0.3–0.5 cùn perpendicular insertion. Moxa: 3 cones; pole 3–5 min.
- Categories: Stream (shù) (wood) point; confluence point (bā mài jiāo huì xué) of the girdling vessel.
GB-43 (侠溪 xiá xī, Pinched Ravine): Located on the dorsal aspect of the foot, proximal to the margin of the web between the fourth and fifth toes, level with the metatarsophalangeal (mtp) articulation of the fourth toe.
- Indications: Headache; dizzy vision; tinnitus; deafness; painful red swollen eyes; rib-side pain; febrile disease; mammary welling-abscess (rǔ yōng).
- Stimulus: Needling: 0.2–0.3 cùn upward oblique or perpendicular insertion. Moxa: 2–3 cones; pole 3–5 min.
- Categories: Spring (yíng) (water) point.