Search in dictionary
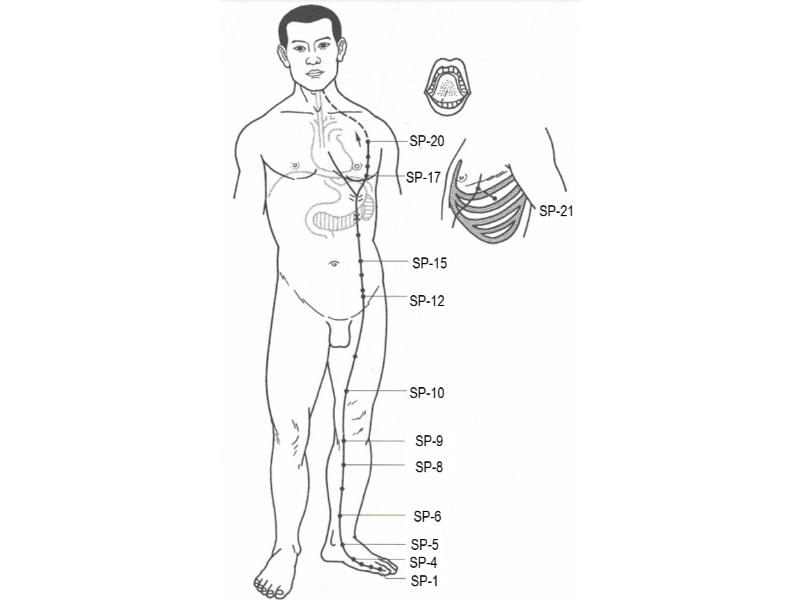
Foot greater yīn (tài yīn) spleen channel
足太阴脾经 〔足太陰脾經〕 zú tài yīn pí jīng
Abbreviation: SP. One of the twelve channels.
 |
| Foot greater yīn (tài yīn) spleen channel |
|---|
Connections
ST → SP → HT; homes to the spleen; nets the stomach.
Spleen Channel Pathway
Overview
Medial tip of the big toe → inside of the foot → inside of the leg → abdomen ð- Homes spleen and nets stomach → side of chest → esophagus → throat → root and underside of tongue.
- Branch: stomach → diaphragm → heart → HT channel.
Description
The foot greater yīn (tài yīn) spleen channel starts on the medial tip of the great toe (SP-1, yǐn bái, Hidden White) and runs up the medial aspect of the foot along the border of the light and dark skin. It then passes in front of the medial malleolus and up the posterior side of the leg along the posterior margin of the tibia. Eight cùn above the medial malleolus, it intersects with and runs anterior to the foot reverting yīn (jué yīn) liver channel. It ascends the medial aspect of the lower leg to the knee and the anteromedial aspect of the thigh.
From here, it passes on to the abdomen, ascending (4 cùn lateral to the midline) to the lower margin of the rib cage, where it homes to the spleen and nets the stomach and veers outward 2 cùn (6 cùn from the midline) to the second intercostal space. It proceeds upward, passes through the diaphragm, ascends to the side of the esophagus, and finally proceeds up to the root of the tongue to disperse over the tongue’s lower surface.
A branch breaks off in the stomach region, crossing the diaphragm to flow into the heart and meet the hand lesser yīn (shào yīn) heart channel.
Spleen Channel Acupoints
Indications of SP Acupoints
The 21 points on the foot greater yīn (tài yīn) spleen channel treat spleen-stomach disease, diseases of the external genitals, and gynecological diseases, as well as problems anywhere on the pathway of the channel.
| Indications for SP Points |
|---|
|
- Spleen and stomach: Pain in the stomach duct and abdomen; vomiting; belching, abdominal distension; sloppy stool or diarrhea; reduced eating; jaundice; generalized heaviness and lack of strength; reversal cold.
- Genitourinary and gynecological: Mounting qì (inguinal hernia); flooding and spotting; menstrual irregularities; amenorrhea.
- External pathway: Swelling of the inner face of the lower limbs.
Major SP Acupoints
SP-6 (三阴交 sān yīn jiāo, Three Yīn Intersection): Located on the medial aspect of the lower leg, 3 cùn superior to the tip of the medial malleolus, on the line connecting the malleolus and SP-9.
- Indications: Rumbling intestines; abdominal distension; diarrhea; menstrual irregularities; vaginal discharge; yīn protrusion (prolapse of the uterus); infertility; difficult delivery; seminal emission; mounting qì (inguinal hernia); enuresis; insomnia; wilting-impediment (wěi bì) of the lower limbs.
- Stimulus: Needling: 0.3–1. 0 cùn perpendicular insertion. Moxa: 3–7 cones; pole 10–30 min.
- Categories: Intersection point (jiāo huì xué) of the three yīn channels of the foot (spleen, liver and kidney); one of the nine needles for returning yáng.
SP-8 (地机 dì jī, Earth’s Crux): Located on the medial aspect of the lower leg, slightly behind the posterior edge of the tibia, 3 cùn inferior to SP-9 on the line connecting the medial malleolus and SP-9.
- Indications: Abdominal distension; diarrhea; inhibited urination; water swelling; menstrual irregularities; menstrual pain; and seminal emission.
- Stimulus: Needling: 0.3–1. 0 cùn perpendicular insertion. Moxa: 3 cones; pole 5–10 min.
- Categories: Cleft point (xī xué) of the spleen channel.
SP-9 (阴陵泉 yīn líng quán, Yīn Mound Spring): Located on the medial aspect of the lower leg, at the inferior border of the medial condyle of the tibia, between the posterior edge of the tibia and the anterior edge of the gastrocnemius muscle.
- Indications: Abdominal distension; diarrhea; water swelling; jaundice; inhibited urination or urinary incontinence; knee pain.
- Stimulus: Needling: 0.5–1. 0 cùn perpendicular insertion. Moxa: 3 cones; pole 3–5 min.
- Categories: Uniting (hé) (water) point.
SP-10 (血海 xuè hǎi, Sea of Blood): Located on the anteromedial aspect of the thigh, in the prominence of the vastus medialis muscle 2 cùn superior and slightly medial to the superior medial corner of the patella.
- Indications: Menstrual irregularities; amenorrhea; flooding and spotting; dormant papules: eczema; cinnabar toxin (dān dú).
- Stimulus: Needling: 0.5–1.2 cùn perpendicular insertion. Moxa: 3–5 cones; pole 5–10 min.
SP-15 (大横 dà héng, Great Horizontal): Located on the abdomen, 4 cùn lateral to the center of the umbilicus.
- Indications: Diarrhea; constipation; abdominal pain.
- Stimulus: Needling: 0.3–1. 0 cùn perpendicular insertion. Moxa: 5 cones; pole 10–30 min.
- Categories: Intersection point (jiāo huì xué) of the spleen channel and yīn linking vessel (yīn wéi mài).